

Fasting is not required before the blood draw. The patient's medications should be reviewed, as these can affect the outcome of the test.

He or she removes the band from the patient's arm, and then removes the needle and applies pressure to the venipuncture site until hemostasis occurs, usually within one minute.
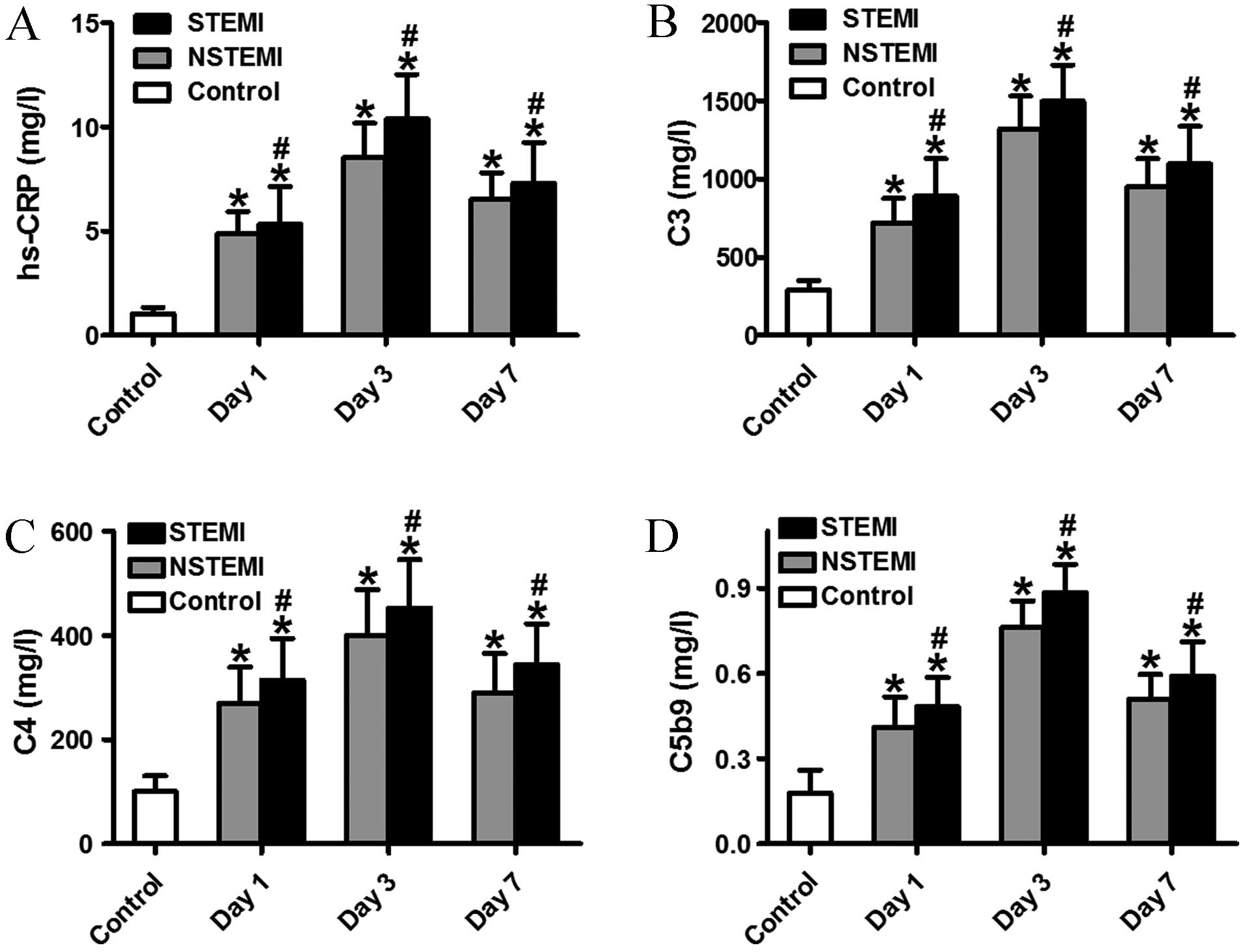
Once the area air dries, the practitioner introduces a needle into the vein and draws a vial of blood. The phlebotomist palpates the vein to confirm the location and cleanses the area with an alcohol prep pad. The phlebotomist secures a snug, rubber band around the upper arm, and the patient pumps his or her fist several times. A phlebotomist performs the procedure in most cases. Specimen CollectionĪ blood specimen is taken from a peripheral venous draw. More modest elevations tend to be associated with a broader spectrum of etiologies, ranging from sleep disturbances to periodontal disease. Trauma can also cause elevations in CRP (alarmin response). However, markedly elevated levels of CRP are most often associated with an infectious cause (an example of pathogen-associated molecular pattern recognition). These include acute and chronic conditions, and these can be infectious or non-infectious in etiology. There are numerous causes of an elevated C-reactive protein. Persistently elevated CRP levels can be seen in chronic inflammatory conditions such as chronic infections or inflammatory arthritides such as rheumatoid arthritis. Īs compared to the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, which is an indirect test for inflammation, the levels of CRP rise and fall rapidly with the onset and removal of the inflammatory stimulus respectively. It can also worsen tissue damage in certain cases by activation of the complement system and thus inflammatory cytokines. It can activate the classic complement pathway and also activate phagocytic cells via Fc receptors to expedite the removal of cellular debris and damaged or apoptotic cells and foreign pathogens. This can become pathologic, however, when it is activated by autoantibodies displaying the phosphocholine arm in auto-immune processes, such as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP). It plays a role in the recognition and clearance of foreign pathogens and damaged cells by binding to phosphocholine, phospholipids, histone, chromatin, and fibronectin. It has been demonstrated to have some protective properties in animal studies on lung tissue in alveolitis by reducing neutrophil-mediated damage to the alveoli and protein leakage into the lung.ĬRP has both proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory properties. There is some question of whether dysregulation of the role of CRP in the clearance of apoptotic cells and cellular debris plays a role in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), but this has not been definitively demonstrated. The name CRP arose because it was first identified as a substance in the serum of patients with acute inflammation that reacted with the "c" carbohydrate antibody of the capsule of pneumococcus.ĬRP is a pentameric protein synthesized by the liver, whose level rises in response to inflammation. CRP is an acute-phase reactant protein that is primarily induced by the IL-6 action on the gene responsible for the transcription of CRP during the acute phase of an inflammatory/infectious process. Also, it could be helpful in monitoring the success of medication in patients with infection.C-reactive protein (CRP) was discovered by Tillett and Francis in 1930. CRP level is usually ordered when there is a possibility that some sort of infection is present in the body, based on the symptomatology of the patient. Quantitative CRP measurement could help in early diagnosis of sepsis. CRP could also be elevated in second half of pregnancy. Elevated quantitative CRP level can be a sign of many conditions such as infection (like pneumonia or tuberculosis), inflammatory bowel disease, autoimmune inflammatory disease (such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis), conditions with severe tissue damage (such as trauma and burns), some sorts of cancer (lymphoma), etc. There are two types of CRP measurement: quantitative CRP and high-sensitive CRP (hs CRP). CRP is synthesized in the liver in response to some factors produced by macrophages (e.g., IL-6). Acute-phase reactants are a group of proteins whose concentrations increase in blood as a response to inflammatory process. Useful in predicting risk for cardiovascular disease.Ĭ-reactive protein (also known as CRP) is one of the acute-phase proteins produced by the liver.
For: Arthritis, General Wellness, Heart Health


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
